EXTRUSION PROCESSES Metal Extrusion Extrusion Design Impact Extrusion MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Metal Casting Metal Forming Metal Rolling Metal Forging Metal Drawing Sheet Metal Powder Processes
Hydrostatic Extrusion
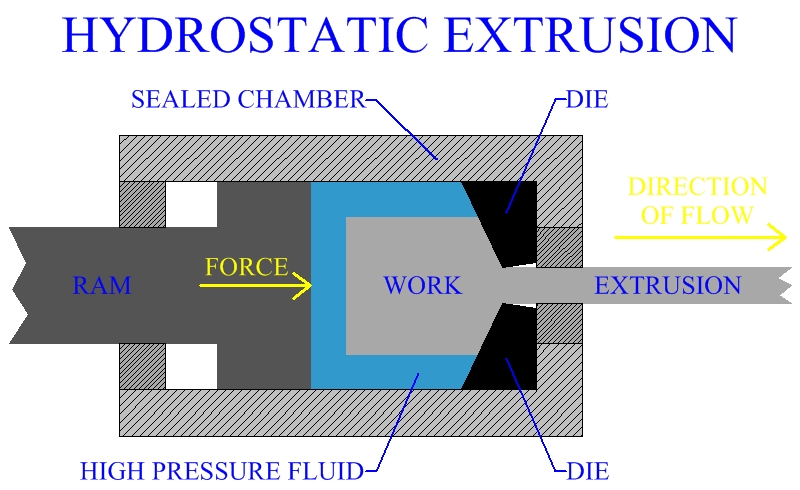
In hydrostatic extrusion the work piece is held in a sealed chamber surrounded by pressurized liquid. Hydrostatic extrusion is actually a form of direct extrusion. The force delivered through the ram is what pressurizes the liquid. The liquid applies pressure to all surfaces of the work billet. When the ram moves forward, it is the force from the incompressible fluid that pushes the work through the die, extruding the metal part.
Figure:234
|
A critical aspect of manufacturing by this process is setup. The metal work billet must first be tapered to fit through the die opening, thus creating a seal. This is done before adding the liquid, in order to prevent leaking. Since the liquid is under great pressure, this taper must be precise to create a robust bond.
Figure:235

|
Many different shapes may be manufactured by this process, using a variety of materials. A significant advantage of hydrostatic extrusion, is that essentially all friction at the work chamber interface is eliminated. Another advantage is that the hydrostatic pressure will increase the ductility of the work, enabling brittle materials to be extruded easier. Liquid pressure from all directions also greatly decreases the chances of buckling of the work. Hydrostatic extrusion may be performed at room or elevated temperatures, depending upon the manufacturing process. When performed hot, the liquid will insulate the work from thermal gradients between the container and work material. An advanced variation of this process, is called fluid to fluid extrusion. This process is basically the same, except that the part is extruded into a second chamber also containing pressurized liquid. The liquid in the second chamber is of a lower pressure than the first. Several different kinds of liquids are used when manufacturing by hydrostatic extrusion, including oils, waxes, melted polymers and molten glass. Hydrostatic extrusion has not had much use in manufacturing industry, due to the complicated equipment and procedures, work preparation, long cycle times and dangers of working with hot, high pressure liquid.