Manufacturing Home
FORGING
PROCESSES
Metal Forging
Drop Forging Hammers
Hydraulic And Mechanical Presses
Metal Piercing
Metal Sizing
Roll Forging
Swaging Or Radial Forging
Metal Hobbing
Metal Ball Forging
Orbital Forging
Ring Forging
Riveting
Metal Coining
Isothermal Forging
Trimming Of Forged Parts
High Energy Rate Forging
MANUFACTURING
PROCESSES
Metal Casting
Metal Forming
Metal Rolling
Metal Extrusion
Metal Drawing
Sheet Metal
Powder Processes
|
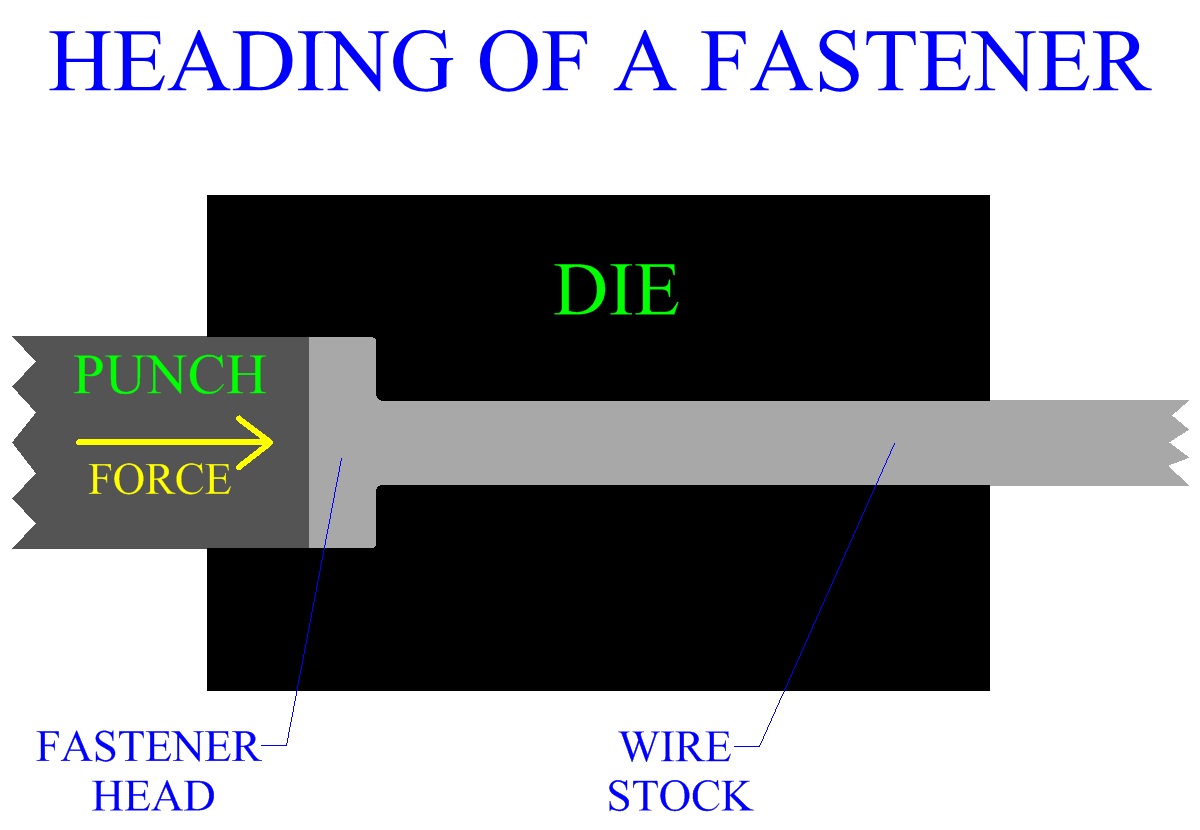
Heading Or Upset Forging
Heading or upset forging is a process by which stock, (typically cylindrical),
is upset at its end in order to increase the cross section of the material in this area.
This metal forging process may be hot, but is often a cold working operation.
Cold working will take advantage of the strengthening of the material in the region
worked. Unlike upsetting, as discussed under open die forging, upset forging can
employ closed die. For typical industrial applications, heading, is mostly performed
horizontally, as shown in the diagrams. Heading is a manufacturing process used
extensively in the production of fasteners that include nails, screws, nuts and bolts.
Due to the enormous quantity of fasteners produced in modern manufacturing industry,
heading is the most commonly used metal forging process in the world today. The
impression in the head may be forged in either the punch, the die, or both.
Figure:183
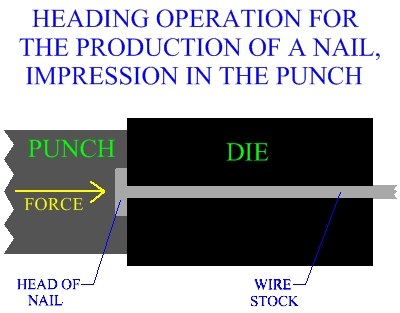
|
Figure:184
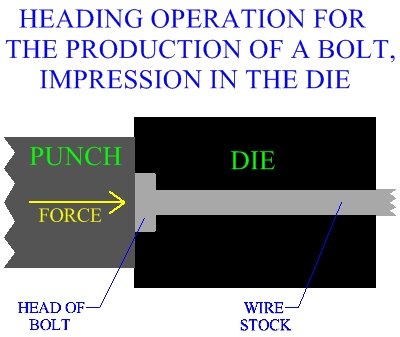
|
Figure:185
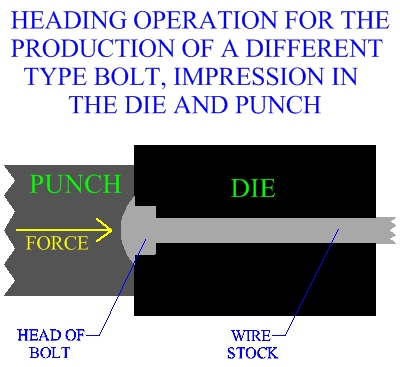
|
In order to ensure proper metal flow during the forging of the head, and thus
avoid bending or buckling of the stock material during compression, the length of
stock to be forged should be less than three times the diameter of the stock.
Figure:186
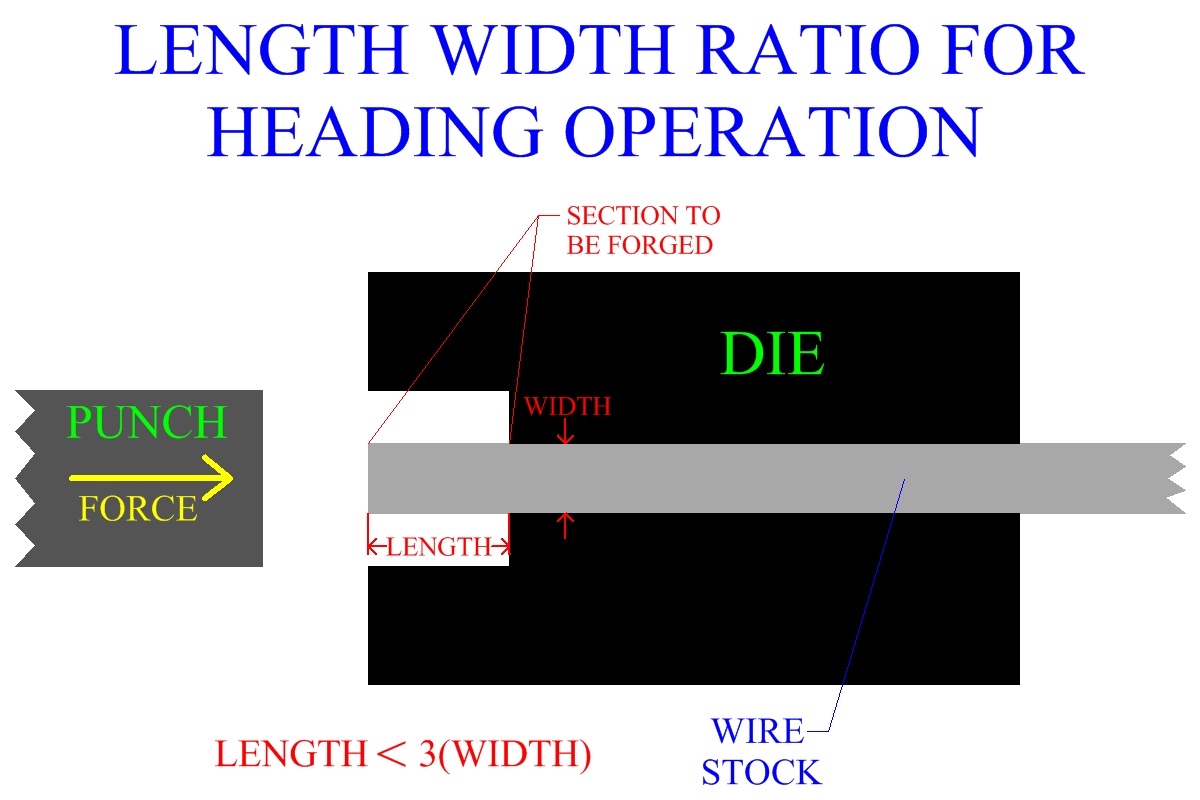
|
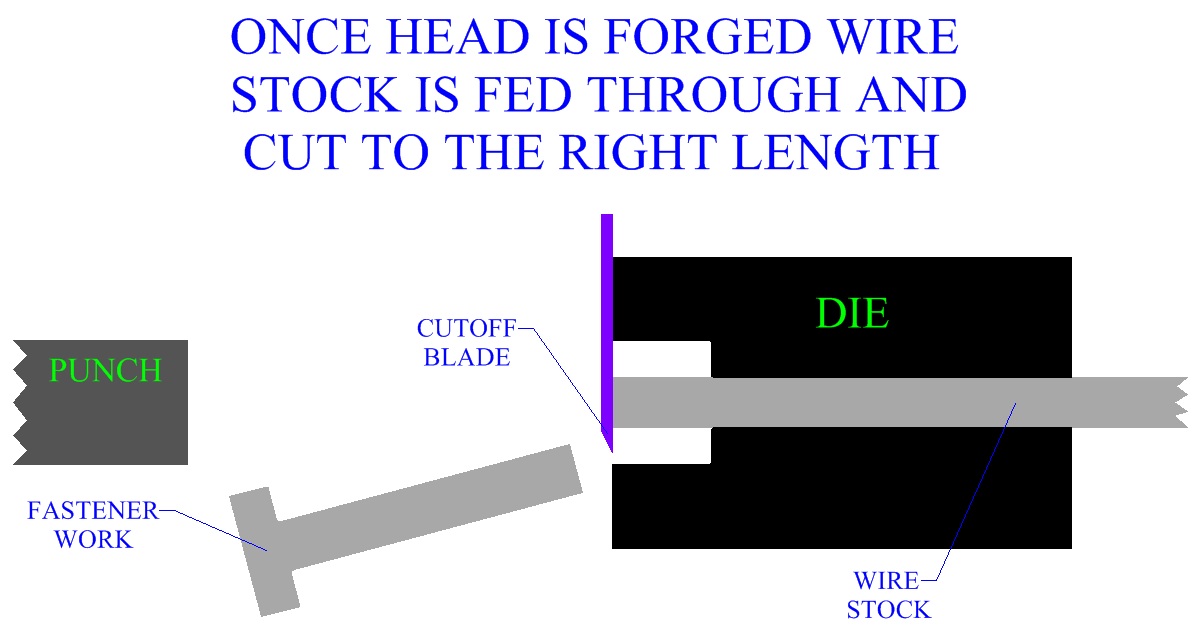
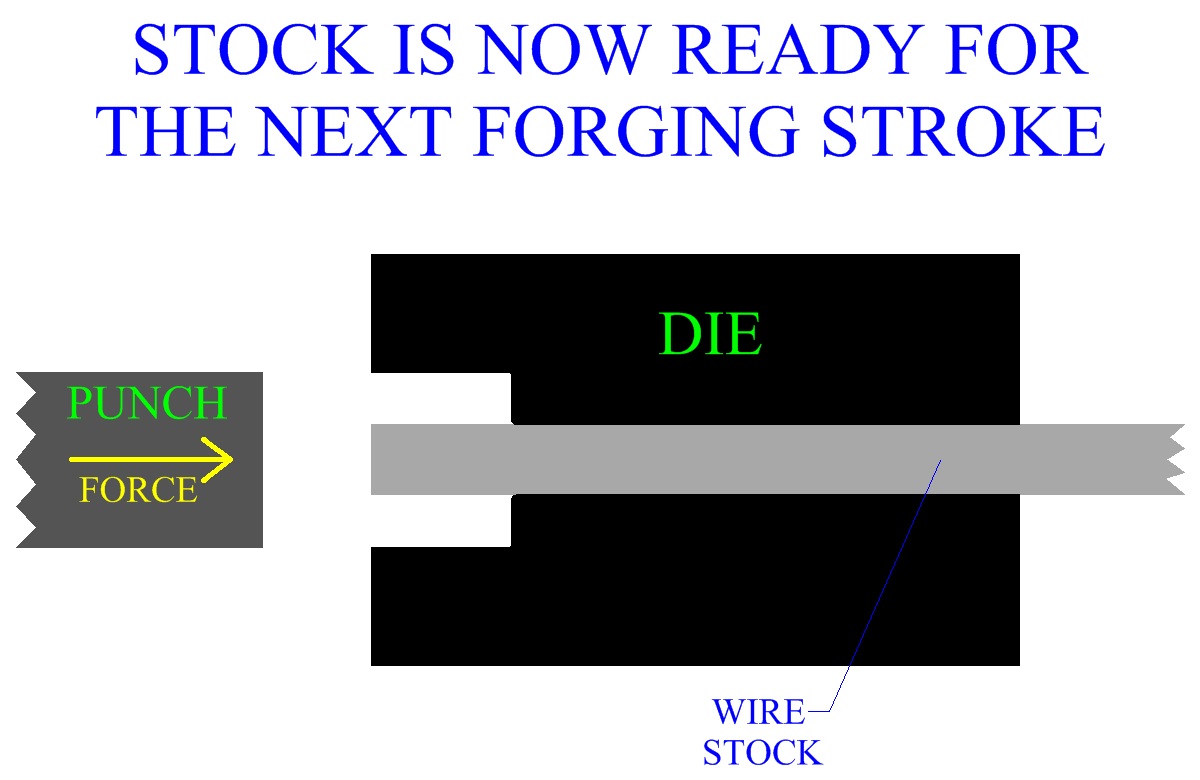
Upset forging, or heading, is a well developed metal working
process in manufacturing industry. Stock is fed through the die, forged, and then cut to length.
Some heading operations can produce up to 300 parts per minute.
Most fasteners will be subject to a further
thread rolling operation to form threads. Thread rolling also has
an extremely high productivity rate.
Figure:187
|
Figure:188
|
Figure:189
|
TOP
|
PRIVACY POLICY
|






