METAL CASTING
PROCESSES
Metal Casting Principles
Metal Casting
Metal Casting Operation
Effect Of Gases On Metal Casting
Metal Casting Design
Expendable Mold Casting
Sand Casting
Plaster Mold Casting
Shell Mold Casting
Vacuum Casting or V-process
Expanded Polystyrene Casting
Investment Casting
Permanent Mold Casting
Basic Permanent Mold Casting
Slush Casting
Pressure Casting
Vacuum Permanent Mold Casting
Die Casting
Hot Die Casting
Cold Die Casting
True Centrifugal Casting
Semicentrifugal Casting
Centrifuge Casting
Ingot Casting
Continuous Casting
MANUFACTURING
PROCESSES
Metal Forming
Metal Rolling
Metal Forging
Metal Extrusion
Metal Drawing
Sheet Metal
Powder Processes
Ceramic Mold Casting
The manufacturing process of ceramic mold casting is like the process of plaster mold casting but can cast materials at much higher temperatures. Instead of using plaster to create the mold for the metal casting, ceramic casting uses refractory ceramics for a mold material. In industry, parts such as machining cutters, dies for metalworking, metal molds, and impellers may be manufactured by this process.
The Process
The first step in manufacture by ceramic mold casting is to combine the material for the mold. A mixture of fine grain zircon (ZrSiO4), aluminum oxide, fused silica, bonding agents, and water, creates a ceramic slurry . This slurry is poured over the casting pattern and let set. The pattern is then removed and the mold is left to dry. The mold is then fired.The firing will burn off any unwanted material and make the mold hardened and rigid. The mold may also need to be baked in a furnace as well. The firing of the mold produces a network of microscopic cracks in the mold material. These cracks give the ceramic mold both good permeability and collapsibility for the metal casting process.
Figure:29 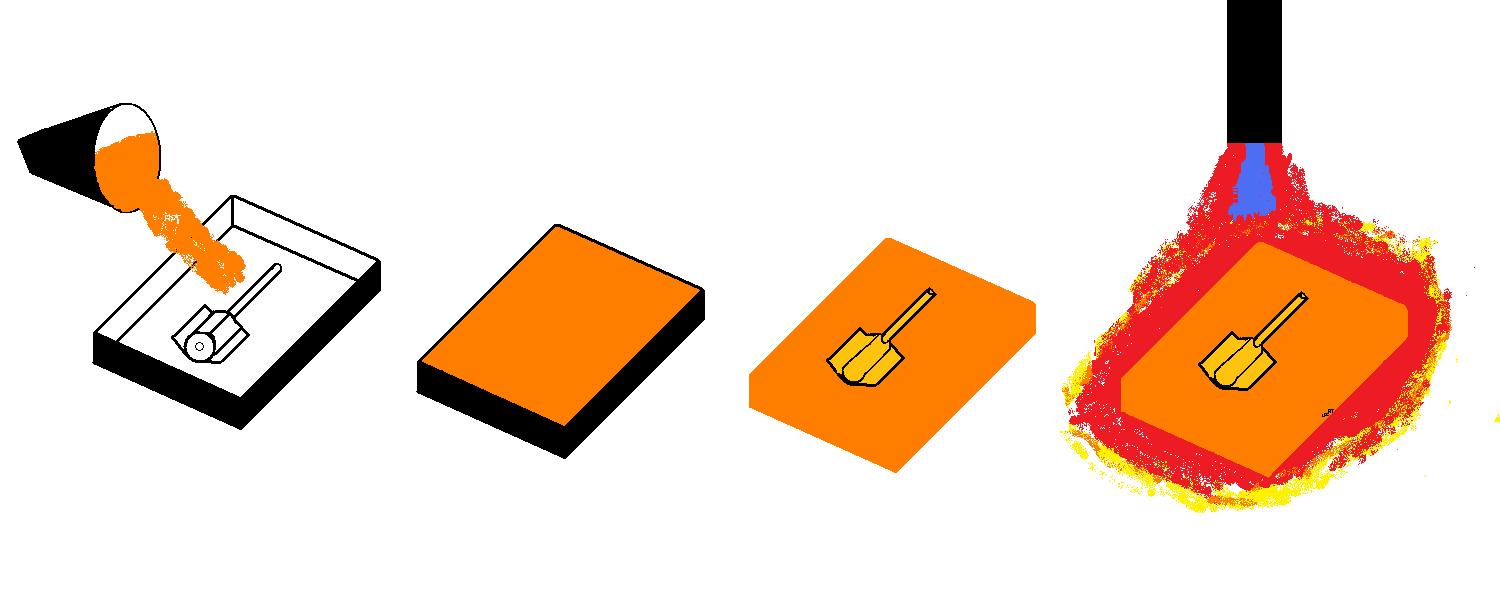
|
Once prepared, the two halves of the mold are assembled for the pouring of the metal casting. The two halves,(cope and drag section), may be backed up with fireclay material for additional mold strength. Often in manufacturing industry, the ceramic mold will be preheated prior to pouring the molten metal. The metal casting is poured, and let solidify. In ceramic mold casting, like in other expendable mold processes, the ceramic mold is destroyed in the removal of the metal casting.
Properties And Considerations Of Manufacturing By Ceramic Mold Casting
- Manufacturing by ceramic mold casting is similar to plaster mold casting in that it can
produce parts with thin sections, excellent surface finish, and high dimensional accuracy.
Manufacturing tolerances between .002 and .010 inches are possible with this process.
- To be able to cast parts with high dimensional accuracy eliminates the need for
machining, and the scrap that would be produced by machining. Therefore precision metal
casting processes like this are efficient to cast precious metals, or materials that
would be difficult to machine.
- Unlike the mold material in the
plaster metal casting process, the refractory mold material in ceramic casting can
withstand extremely elevated temperatures. Due to this heat tolerance, the ceramic casting
process can be used to manufacture ferrous and other high melting point metal casting
materials. Stainless steels and tool steels can be cast with this process.
- Ceramic mold casting is relatively expensive.
- The long preparation time of the mold makes manufacturing production rates
for this process slow.
- Unlike in plaster mold casting, the ceramic mold has excellent permeability due
to the microcrazing, (production of microscopic cracks), that occurs in the firing
of the ceramic mold.