METAL CASTING PROCESSES Metal Casting Principles Metal Casting Metal Casting Operation Effect Of Gases On Metal Casting Metal Casting Design Expendable Mold Casting Sand Casting Plaster Mold Casting Ceramic Mold Casting Shell Mold Casting Vacuum Casting or V-process Investment Casting Permanent Mold Casting Basic Permanent Mold Casting Slush Casting Pressure Casting Vacuum Permanent Mold Casting Die Casting Hot Die Casting Cold Die Casting True Centrifugal Casting Semicentrifugal Casting Centrifuge Casting Ingot Casting Continuous Casting MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Metal Forming Metal Rolling Metal Forging Metal Extrusion Metal Drawing Sheet Metal Powder Processes
Expanded Polystyrene Casting
In the expanded polystyrene casting process, a sand mold is packed around a polystyrene pattern representing the metal casting to be manufactured. The pattern is not removed, and the molten metal is poured into the pattern which is vaporized from the heat of the metal. The liquid metal takes the place of the vaporized polystyrene and the casting solidifies in the sand mold.
In metal casting industry this process is known as the lost-foam process, evaporative pattern casting, or the full mold process. A large variety of castings of different sizes and materials can be manufactured using this technique. Parts produced in manufacturing industry using this process include crankshafts, cylinder heads, machine bases, manifolds, and engine blocks.
The Process
The first step in the evaporative casting process is to manufacture the polystyrene pattern. For small production runs, a pattern may be cut from larger sections of polystyrene material and assembled together. For large industrial manufacturing processes, the pattern will be molded. A die, often made from aluminum, is used for this process. Polystyrene beads are placed in the die and heated, they expand from the heat and the foam material takes the shape of the die.Depending upon the complexity of the casting, several of these polystyrene sections may have to be adhered together to form the pattern. In most cases the pattern is coated with a refractory compound, this will help create a good surface finish on the metal casting. In addition to the casting itself, the foam pattern will also include the pouring cup and gating system.
Figure:44
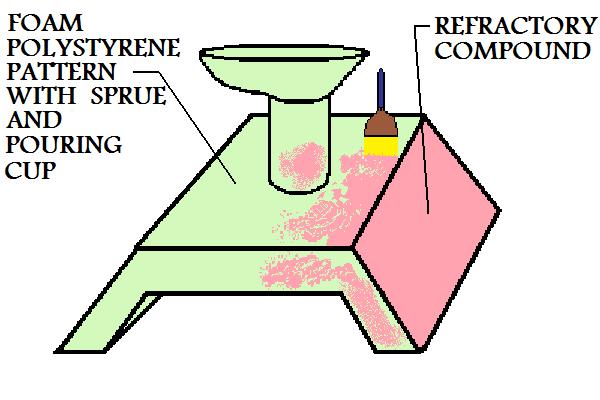
|
The pattern is then placed in a flask and molding sand is packed around it. The sand may or may not contain bonding agents, dependent upon the particular manufacturing procedure.
Figure:45
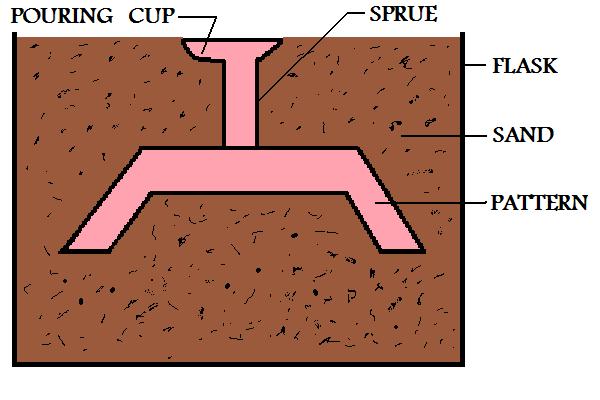
|
The molten metal is then poured into the mold without removing the pattern. The liquid metal vaporizes the polystyrene pattern, as it flows through the mold cavity. Any left over product from the vaporized polystyrene material is absorbed into the molding sand.
Figure:46
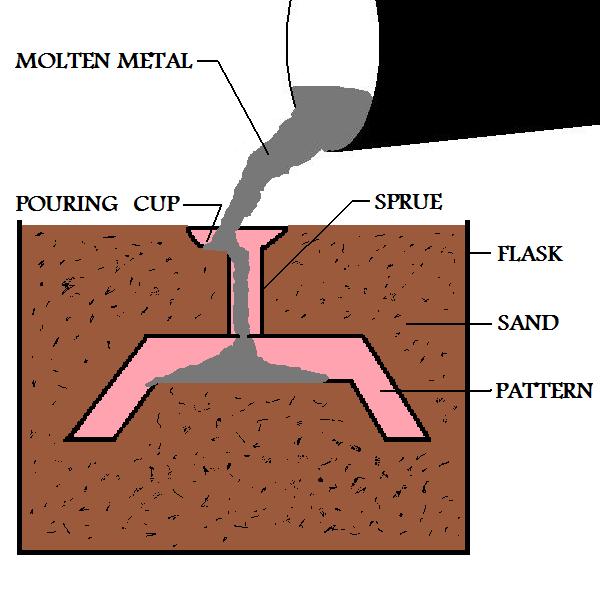
|
The molten metal is then allowed to harden within the sand mold. Once solidified, the casting is removed.
Figure:47
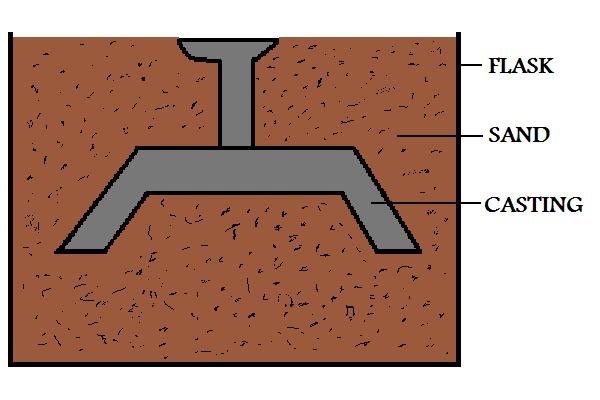
|
Properties And Considerations Of Manufacturing By Expanded Polystyrene Casting
- If a core is need it is incorporated within the pattern. Therefore placing and securing a core in the mold cavity before the pouring of the metal casting is not a step in this manufacturing process.
- Flasks for this process are simple and not expensive. Also the manufacturing process itself is easy, since there is no parting line or removal of the pattern needed.
- In manufacturing industry, patterns for expanded polystyrene metal casting will always include the full gating system.
- Due to the extra energy required to vaporize the polystyrene, there will be a large thermal gradient present at the metal-pattern interface as the casting is being poured.
- Very complex metal casting geometry can be produced using this process.
- This manufacturing process can be very efficient in the production of metal castings for large industrial runs. The main cost is to create the die to produce the foam polystyrene patterns. Once that is overcome, the process itself is very inexpensive.
- This manufacturing process can be easily automated.