METAL CASTING PROCESSES Metal Casting Principles Metal Casting Metal Casting Operation Effect Of Gases On Metal Casting Metal Casting Design Expendable Mold Casting Sand Casting Plaster Mold Casting Ceramic Mold Casting Shell Mold Casting Vacuum Casting or V-process Expanded Polystyrene Casting Investment Casting Permanent Mold Casting Basic Permanent Mold Casting Slush Casting Vacuum Permanent Mold Casting Die Casting Hot Die Casting Cold Die Casting True Centrifugal Casting Semicentrifugal Casting Centrifuge Casting Ingot Casting Continuous Casting MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Metal Forming Metal Rolling Metal Forging Metal Extrusion Metal Drawing Sheet Metal Powder Processes
Pressure Casting
Pressure casting, also known in manufacturing industry as low pressure casting or pressure pouring, is another variation of permanent mold casting. Instead of pouring the molten metal into the casting and allowing gravity to be the force that distributes the liquid material through the mold, pressure casting uses air pressure to force the metal through the gating system and the metal casting's cavity. This process can be used to cast high quality manufactured parts. Often steel castings are cast in graphite molds using this process. For example, in industry, steel railroad car wheels are cast with this method.
The Process
This is a permanent mold process and the manufacture of the mold in pressure casting is standard in most regards, see basic permanent mold casting. Two blocks are machined extremely accurately, so they can open and close precisely for removal of metal parts. The casting's gating system is machined into the mold. The gating system is set up so that the molten material flows into the mold from the bottom instead of the top, (like in gravity fed processes).
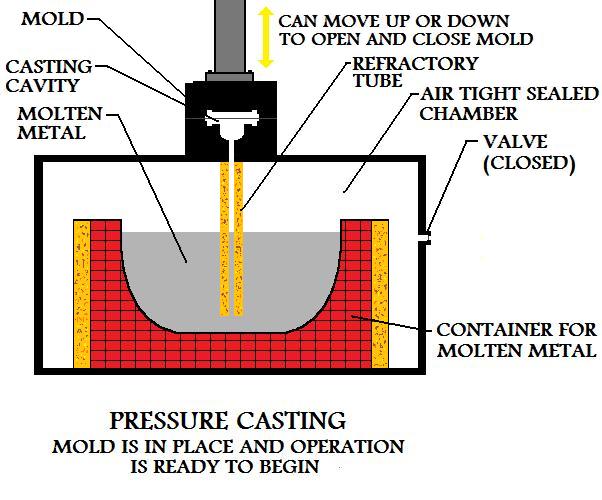
The mold is set up above the supply of liquid metal to be used for the casting. A refractory tube goes from the entrance of the gating system down into the molten material.
Figure:74
|
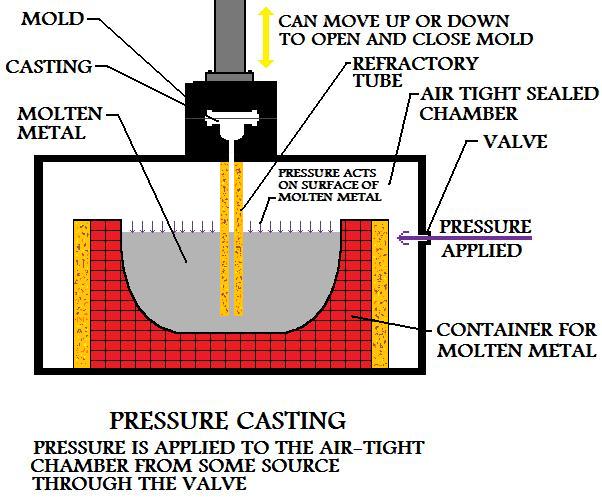
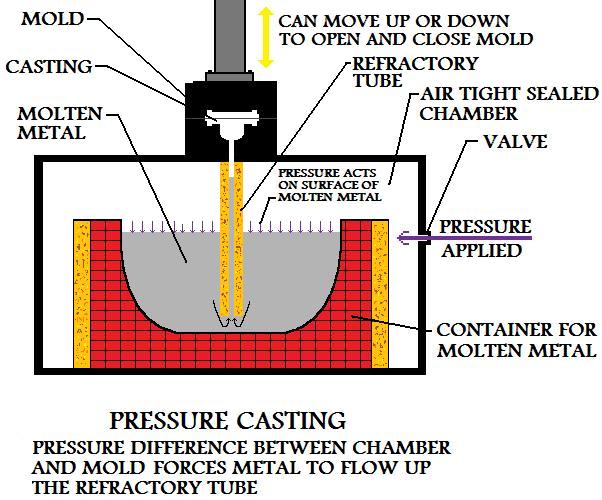
During manufacture by this process, the chamber that the liquid material is in is kept air tight. When the mold is prepared and ready for the pouring of the metal casting, air pressure is applied to the chamber. This creates pressure on the surface of the liquid, that in turn forces molten material up the refractory tube and throughout the mold.
Figure:75
|
Pressure used in pressure casting is usually low, 15lbs/in2 could be typical for industrial manufacture using this process.
Figure:76
|
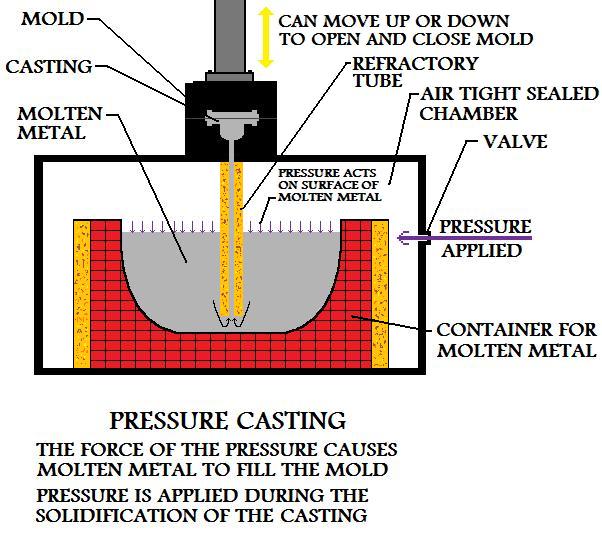
The air pressure is maintained until the metal casting has hardened within the mold. Once the cast part has solidified, the mold is opened and the part is removed.
Figure:77
|
Properties And Considerations Of Manufacturing By Pressure Casting
- Pressure casting manufacture can be used to produce metal castings with superior mechanical properties, good surface finish, and close dimensional accuracy.
- Like in other permanent mold methods, the mold needs to be able to open and close for removal of the work piece. Therefore, very complicated casting geometry is limited.
- Since the refractory tube is submersed in the molten material, the metal drawn for the casting comes from well below the surface. This metal has had less exposure to the environment than the material at the top. Gas trapped in the metal as well as oxidation effects are greatly reduced.
- The high setup cost makes pressure casting not efficient for small runs, but an excellent productivity rate makes it suitable for large batch manufacture.