Slush Casting
Slush casting is a variation of permanent mold casting that is used to
produce hollow parts. In this method neither the strength of the part nor its internal geometry can
be controlled accurately. This metal casting process is used primarily to manufacture toys and parts that
are ornamental in nature, such as lamp bases and statues.
The Process
When producing a cast part using the slush casting method, a permanent mold is employed and
set up. See basic permanent mold casting .
The mold is clamped together and prepared for pouring.
Figure:64

|
After pouring the mold will set, as solidification begins to take place.
Figure:65

|
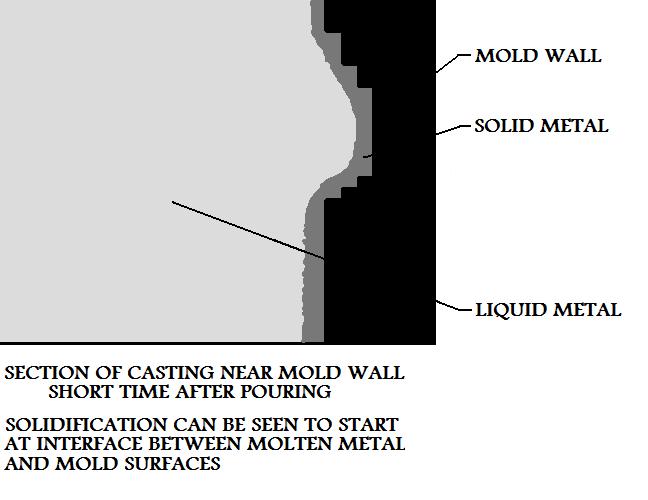
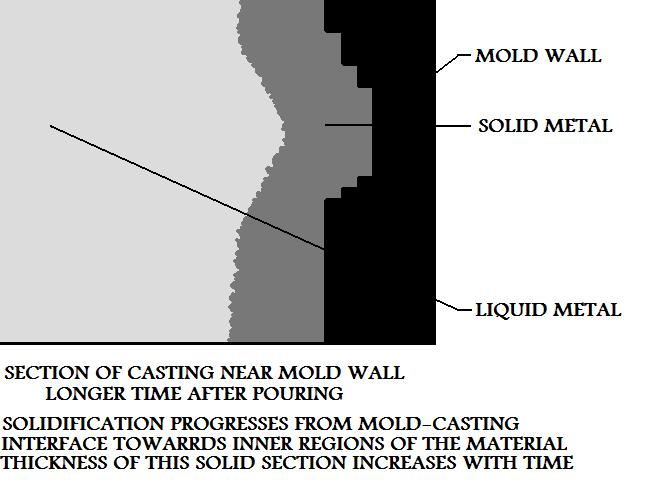
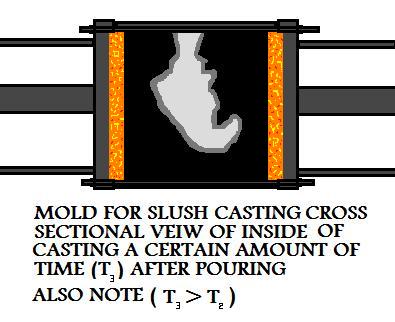
The main principle of this casting process relies on the fact that when a metal casting
hardens in a mold, it will solidify from the mold wall towards the inside of the casting. In
other words a metal skin forms first, (as the external geometry of the part). This skin
thickens as more of the metal casting's material converts to a solid state.
Figure:66
|
Figure:67
|
Figure:68
|
Figure:69
|
Figure:70
|
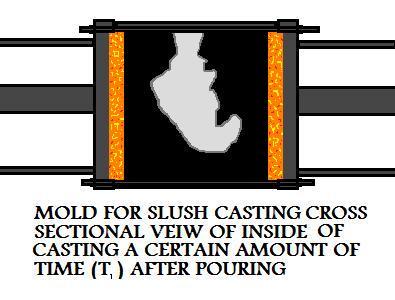
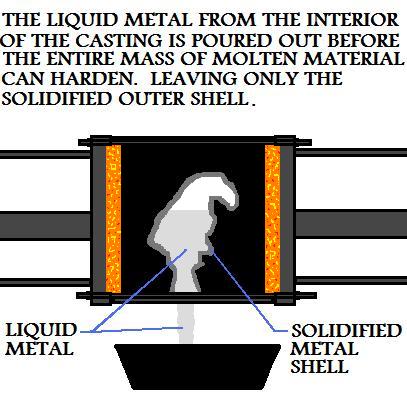
In slush mold casting, during the solidification of the material, when the solid-liquid boundary
has reached a certain point, the mold is turned over and the remaining liquid metal from the casting
is poured out.
Figure:71
|
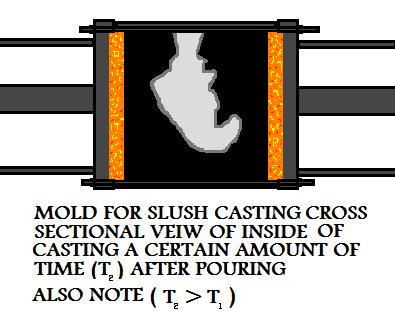
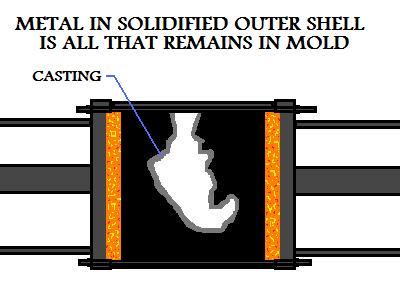
This will leave only the solidified skin with the exterior geometry of the metal cast part and a
hollow interior. The longer the metal casting was allowed to solidify before pouring out the excess
metal, the greater the casting's wall thickness will be.
Figure:72
|
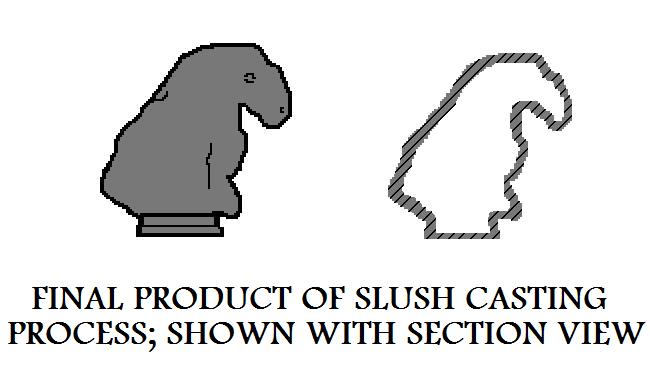
The cast part is then removed from the die and allowed to cool.
Figure:73
|
Properties And Considerations Of Manufacturing
By Slush Casting
- Slush casting is a type of permanent mold casting, therefore many of the basic
principles of a permanent mold process will apply.
- Slush casting is mainly suited to lower melting point materials, zinc, tin, or
aluminum alloys are commonly slush cast in manufacturing industry.
- With this process you need to have a mechanical means of turning over the
mold in order to pour out the molten metal from the cast part.
- When manufacturing by slush casting it is difficult to accurately control the
metal casting's strength and other mechanical properties.
- The casting's internal geometry cannot be effectively controlled with
this process.
- The hollow metal castings manufactured by this process are lighter than solid
parts and save on material.
- Good surface finish and accurate exterior geometry are possible with the
slush casting manufacturing process.
TOP
|









